Estimated Time: 25 minutes
1. Preface
Up until now, we’ve focused on the deployment of applications. But as we know, applications often use backing services: databases, message brokers, and other applications' services (to name a few).
In this lab, you’ll have the opportunity to experiment with both managed services and user-provided services: you’ll create a mysql backing service to persist information about attendees, and you’ll create a user-provided service to allow one application to consume the services of another without hard-coding its route.
In the process, you’ll learn new cf commands: create-service, create-user-provided-service, and bind-service. Don’t forget: cf help is there to help us understand how to invoke each command.
2. Exercises
2.1. Review articulate dependencies
articulate exposes functionality to add attendees on the Services page. However, articulate doesn’t do this alone. It makes REST calls to the attendee-service application. To learn more about services, let’s provision the attendee-service application.
2.2. Push the attendee-service application
-
Download the
attendee-serviceapplication. Copy the file to folder:~/pivotal-cloud-foundry-developer-workshop/attendee-service/(~is shorthand for the home directory in Linux, Mac and Unix based operating systems). You will need to create this directory in your home directory.If your browser warns you about downloading this file please proceed to download it. Source is not required, but you may be curious how it works as you move through the labs.
-
Push the
attendee-serviceapplication.cd ~/pivotal-cloud-foundry-developer-workshop/attendee-service/..and:
cf push attendee-service -p ./attendee-service-0.1.jar -m 512M --random-routeDoes
attendee-servicestart up correctly? Why not?
2.3. Add a Managed Service
-
Review the documentation on managing service instances
-
Review what services are available in the marketplace.
cf marketplace -
There exist two distinct Cloud Foundry managed services that provision MySQL databases:
-
p-mysql is a Pivotal product, and
-
cleardb is a company that specializes in cloud-based MySQL instances
Pivotal Web Services offers the cleardb managed service in its marketplace.
cf create-service cleardb spark attendee-mysqlIf working in a Pivotal Cloud Foundry environment that is not PWS, you are likely to have the p-mysql managed service.
cf create-service p-mysql 100mb attendee-mysql
-
-
Now we need to bind the application with the service instance.
cf bind-service attendee-service attendee-mysqlYou can ignore the TIP: Use 'cf restage attendee-service' to ensure your env variable changes take effect message at this time. -
Restart the application.
cf restart attendee-service -
View the
attendee-servicein a browser.You should see a response similar to the following (the output in the screenshot is rendered by the JSON Formatter for Chrome):
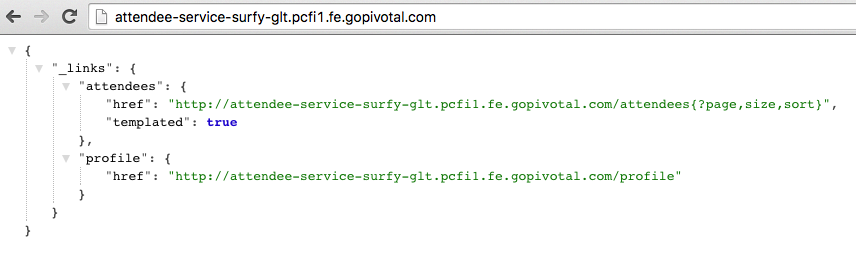
The root endpoint of this application is rather uninteresting. Instead, visit the
/attendeesendpoint. An http GET to theattendeesendpoint will fetch all attendees in the database and display them in JSON format. Note that in the response, thetotalElementsis currently 0.This application implements a RESTful API. This means that you should be able to submit http POST to the same
attendeesendpoint with a body containing the JSON representation of theAttendeemodel type to create such a record. This can be done programmatically, or via REST client tools such as Postman or command-line tools such as curl or httpie. Here’s an example using httpie:http post {{attendees_app_uri}}/attendees firstName=Eitan lastName=Suez emailAddress=esuez@pivotal.io
2.3.1. Questions
-
After binding a service to an application why is the application restarted/restaged?
-
In this case, why could we
restartvsrestage?
2.4. Add a User-Provided Service Instance
In the enterprise, not all services will be provisioned by Pivotal Cloud Foundry.
For example, consider your Oracle RAC cluster. How can we connect our applications running on Pivotal Cloud Foundry to these external systems?
Additionally, how can we easily connect applications together running on the platform?
articulate’s default configuration for the attendee-service uri is http://localhost:8181/. The subsequent steps will allow you to override the default configuration with your own.
-
Read about user-provided service instances.
-
Create a user-provided service instance.
cf create-user-provided-service attendee-service -p uriThis will create an interactive prompt. For the value of
uri, enter yourattendee-serviceapplication's base url:uri> https://{{attendees_app_uri}}/ -
Bind
articulateto theattendee-serviceuser-provided service.cf bind-service articulate attendee-serviceYou can ignore the TIP: Use 'cf restage articulate' to ensure your env variable changes take effect message at this time. -
Restart the application.
cf restart articulate -
Refresh the
articulateServices page. You can now see theattendee-servicelisted underServices.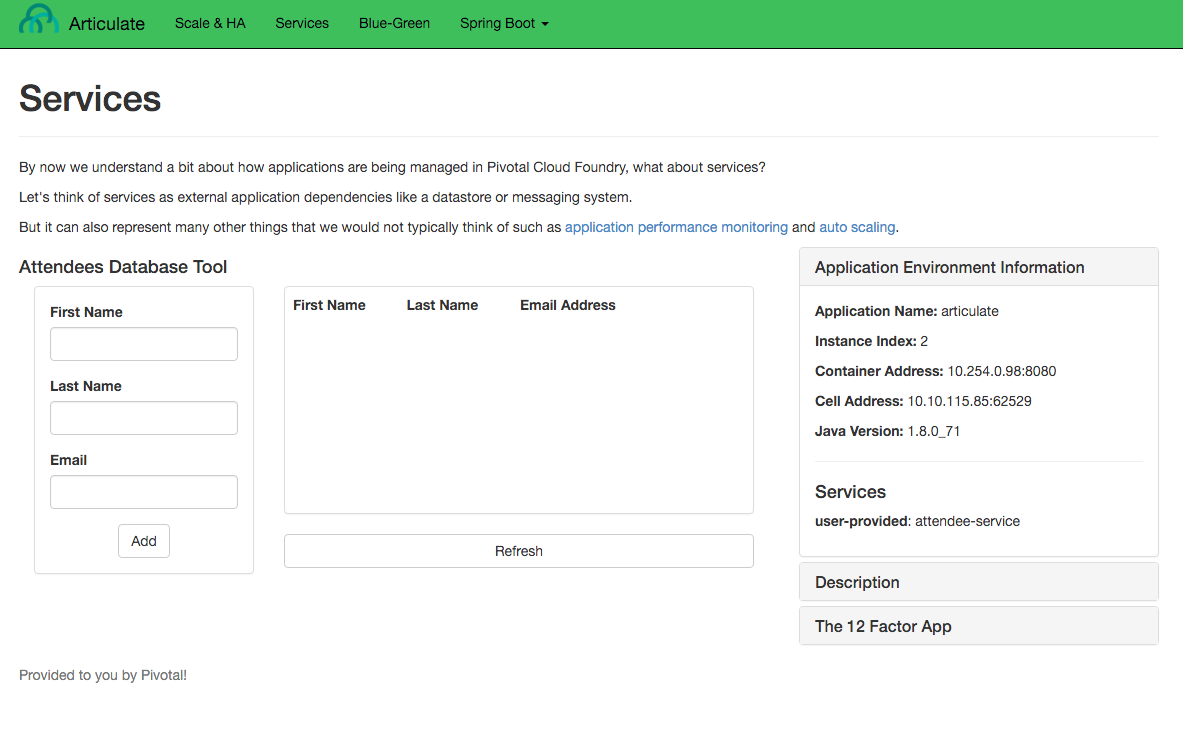
-
Review the environment.
cf env articulate -
Add some attendees.
If you can’t add attendees, review the articulatelogs and the user-provided service instance configuration.
2.4.1. Questions
-
From an application perspective, are managed services instances different from user-provided service instances?
3. Beyond the class
-
Use Spring Music and a User Provided Service Instance to connect to a database (MySQL or Oracle) in your environment.